Jens Juel, Self portrait at an easel. Oil on canvas, 1766. Royal Academy of Fine Arts, Denmark.
Once again, I’m looking into artists’ materials and techniques, though instead of trying to kit myself out for the early Federal era, I’m digging into the last half (quarter) of the 18th century. It seems to be a time of rapid transitions in art materials as new pigments and media are developed. While Mr. Juel is beginning a work in oils, we still see some of the same tools that a watercolorist would use. Brushes, though his are shaped for working in oil; a shell, perhaps to combine pigment with medium, and bags of paint.
Before collapsible tubes were invented in 1841, artists scooped or scraped pigments mulled with medium into skin bags, secured them with twine or string, and then poked a hole in the bag to extrude pigment. Some more clever sorts would plug the hole with a cork– untying the bag would make more of a mess than a distribution system– but otherwise, you risked having your paint dry before you could use it up. Clearly there were some inefficiencies built into the system. (I think it also helps explain why “thick” paintings, that is, paintings using exuberant and textured layers of paint, do not appear until after collapsible tubes are invented and in wide use.)

Matthew Pratt, The American School. oil on canvas, 1765. Metropolitan Museum of Art, Gift of Samuel P. Avery, 1897, 97.29.3
In Pratt’s American School, we can see how small the palettes are, and how small the dots of paint are compared to the pools where colors have been mixed. The easel, presented from another angle, offers clues to the adjustable pegs and triangular/tripod shape of the main support. But what of watercolors?

Winsor & Newton Old Paints: note the tiny bags of paint.
To date, I’ve found conservation reports more helpful than anything else, especially those analyzing paint content for sugars and gums. (One of the keys to watercolors was the re-wettable aspect of the colors; gum arabic, gum tragacanth and honey or sugar were ingredients used in varying proportions to achieve what we now take for granted.) The first watercolor cakes or blocks are introduced in 1780 by William Reeves; often, these were very hard, and had to be agitated in water (ground on a surface) to be used, much like sumi-e ink. Once paint was ground with water, it could be dried in a dish or container for re-wetting and later use. The question of course is, what do dry it in? How do you mix and use the paint?

Caroline Schetky Richardson’s Paint Box
about 1820–30. MFA Boston. 1995.156.1
Mixing is simpler to solve: a palette, of course. The small, dirty-looking oval in the image above is the ivory palette used by Caroline Schetky Richardson; while her box is 1820-1830, it’s still very similar to box in Charles Willson Peale’s portrait of his brother James (below). The box is 21 inches wide, 10 inches high, and 13 inches deep. That makes the palette something like 3 inches wide, if we take a drawer as five inches wide.

James Peale painting a miniature. Oil on canvas by Charles Willson Peale, 1795. Meade Art Museum, Amherst, MA
In the CWP portrait of JP, the slightly open drawer of the painting stand may be giving us a peek at his palette; the simple tumbler of water helps confirm that he is working in watercolor on ivory, and give us a sense of what kind of water container artists used– which, happily, can be more easily sourced than Mr Peale’s box.
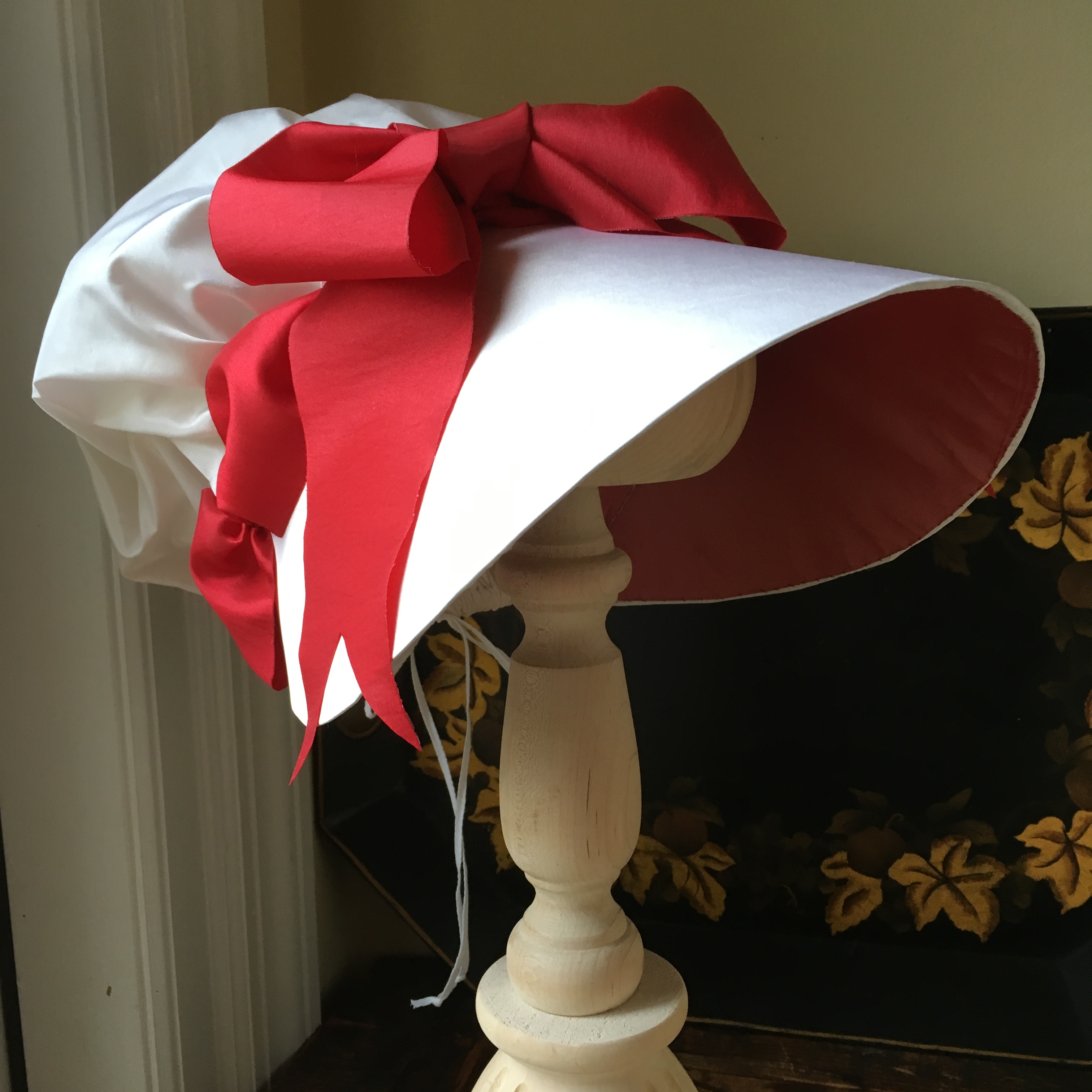
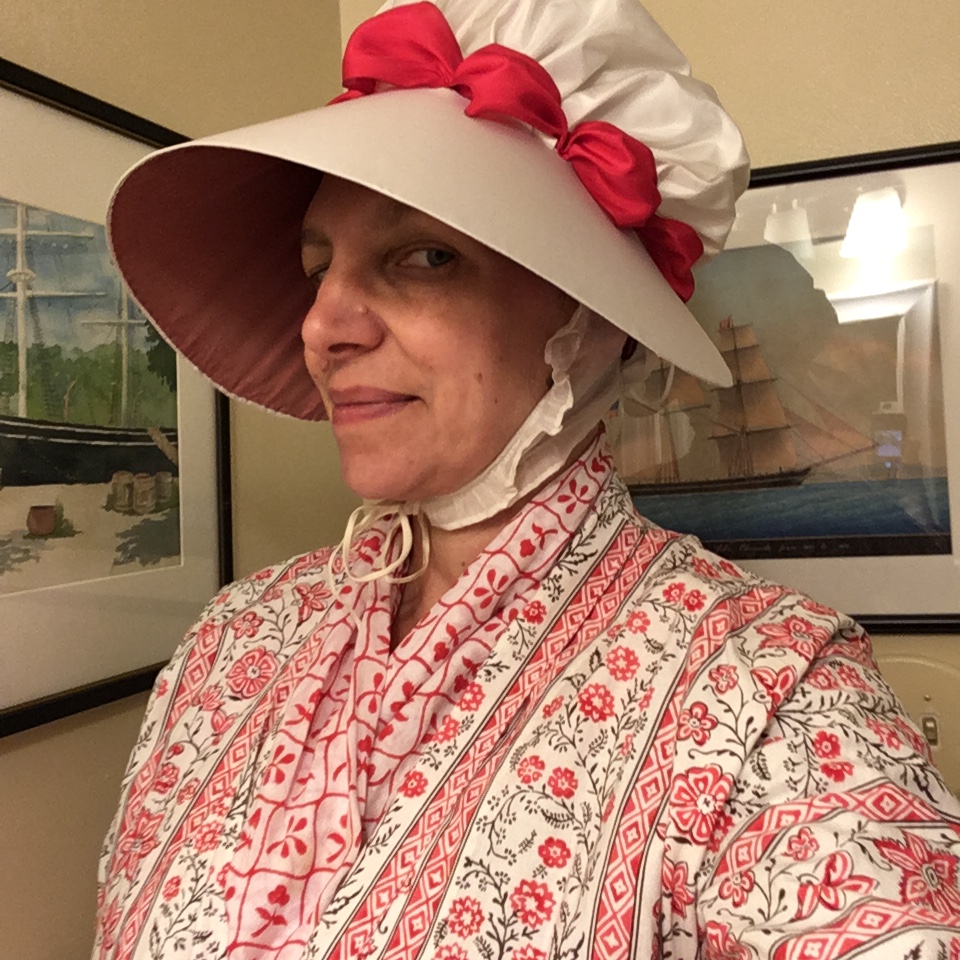

























 Those are hard to unpack: how will other people remember us? Often, we have no idea what we mean to other people, even the ones closest to us. It’s easier for me to know what I would take or keep to remember someone else by– a single sleeve link; a wooden train engine; a stainless steel spoon; a necklace of handmade beads. None of those things reflects what is truly meaningful to me about them, that is, without my knowledge, these aren’t particularly interesting or aesthetic objects. What makes them special is the story I attach to them.
Those are hard to unpack: how will other people remember us? Often, we have no idea what we mean to other people, even the ones closest to us. It’s easier for me to know what I would take or keep to remember someone else by– a single sleeve link; a wooden train engine; a stainless steel spoon; a necklace of handmade beads. None of those things reflects what is truly meaningful to me about them, that is, without my knowledge, these aren’t particularly interesting or aesthetic objects. What makes them special is the story I attach to them.

